Testosterone Replacement Blood Test Targets
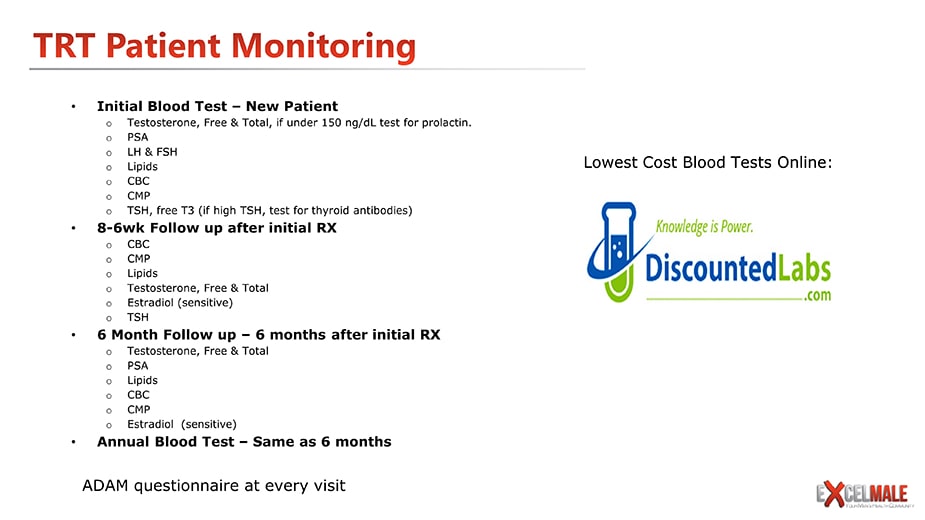
Testosterone Replacement Monitoring Targets and Their Management
(Consult Your Physician Before Any Treatment Initiation, Cessation or Changes). These are not absolute values and should be taken into context with symptoms.
| Total Testosterone Test above 500 ng/dL | If low or hypogonadal symptoms are not improved, increase the testosterone dosage. High T levels (over 1500 ng/dL) with high hematocrit, low HDL and/or side effects may require dosage reduction. |
Free Testosterone ≥ 2 % of total T |
If low, test for sex hormone-binding globulin. Higher TRT dose may increase free T by decreasing SHBG. Low SHBG may be present in diabetes. |
Hematocrit ≤ 53 % |
If high, donate blood or ask your doctor for therapeutic phlebotomy order. If low, investigate anemia or stop donating blood more than every 3 months. High Hematocrit Risks |
PSA ≤ 4 ng/mL |
If high, talk to your doctor about potential prostatic infection or a referral to a urologist. TRT is contraindicated if PSA is 4 ng/mL or greater. |
Estradiol (UltraSensitive Test) = 20- ? pg/mL |
Most men on TRT do not need to use an aromatase inhibitor like anastrozole (Arimidex). Some physicians prescribe low dose anastrozole for what they consider high estradiol. If low, higher testosterone dose and/or cessation of AI may be required. The lab range was derived from men with heart disease and low testosterone, so there is still debate on what the range should be for men on TRT since 0.3 to 0.4 % of testosterone aromatizes to estradiol, so men with high T due to TRT will have higher estradiol. No upper range value has been determined for men on TRT. Studies have shown that for gynecomastia to occur, high estradiol in the presence of low T and high IGF-1 may be required. Read Estradiol In Men – Why Is It Important For Optimal Health And Fitness Performance and The Top 18 Things You Did not Know About Estradiol in Men |
Blood pressure ≤ 135/85 mmHg |
If high, weight loss, exercise, T dose reduction and/or blood pressure medications may be needed. If too low, blood pressure medication dose needs to be reduced, electrolytes checked or hypoglycemia excluded. |
Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate (eGFR) (kidney function)≥ 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 |
If low, good hydration, use of blood pressure medications, and/or stopping offending oral supplements may improve eGFR. Exercise, high protein intake, creatine supplements, and higher muscle mass can also increase creatinine and decrease eGFR. If under 60, explore getting a Cystatin C test. |
Liver enzymes ≤ 1.2 x top value of reference range |
If high, stopping oral supplements can help. AST and ALT can increase with exercise but this is not clinically relevant. If high AST and ALT, test GGT and bilirubin to ensure no liver toxicity is present. |
TSH ≤ 2.5 U/mL |
If high, test for other thyroid tests included in a thyroid panel like free T3, free T4, and antibodies to detect hypothyroidism. Why Only Using TSH to Diagnose Hypothyroidism is Wrong |
Free T3 ≥ 3.7 pg/mL |
If low, hypothyroidism may be present. See comment on TSH. If high (>5 pg/mL), explore hyperthyroidism. |
Ferritin 55-270 ng/mL & Iron 55-160 micrograms/dL |
If low, reduce the frequency of blood donations or phlebotomies and supplement with iron until it is back to normal. If high, donate blood or get therapeutic phlebotomy. |
HDL ≥ 40 mg/dL |
The most difficult parameter to manage. Higher TRT doses decrease HDL. Niacin may help increase HDL but may cause flushing. |
Prolactin ( ≤ 30 nd/dL) |
Test if Total Testosterone is below 150 ng/dL before TRT to detect potential pituitary adenoma or other issues. High levels (> 30 ng/dL) may cause sexual dysfunction and galactorrhea in men (milk production) |
Here are panels that include these tests: Discounted Labs Panels
Buy a testosterone test on DiscountedLabs.com

Nelson Vergel is a chemical engineer who started his search for cutting-edge health knowledge when he was diagnosed with HIV over 30 years ago. Instead of giving into the hopelessness of the deadly diagnosis, he pushed himself to explore therapies to combat wasting syndrome to save his life and those of his peers. He reviewed medical literature and attended numerous health conferences, eventually becoming an advocate member in the National Health Institute (NIH), pharmaceutical research committees, and FDA review panels. To spread survival knowledge, he has given health-related lectures, providing over 700 of them since 1987. Nelson has created popular health forums with over 55,000 members, a health podcast , numerous videos, and has networked with many progressive clinicians. He has been a speaker for 14 pharmaceutical companies on hormones...
- Affordable Blood Tests (16)
- Anemia Tests (1)
- Annual Physical Tests (1)
- Blood Type (1)
- Bodybuilder Blood Work (14)
- Bodybuilder lab tests (9)
- Buy Blood Tests Online (12)
- CBC Lab Panel (12)
- CMP test panel (14)
- CPK Levels (1)
- Cancer Tests (2)
- Celiac Disease Tests (1)
- Cholesterol (6)
- Coagulation Tests (1)
- Consumer Advocacy (2)
- Cost of Blood Work (5)
- Coupons (1)
- DHEA Lab Test (2)
- DHT Test Information (2)
- Diabetes Lab Tests (5)
- Discount Lab Tests (13)
- Discounted Labs Coupons (2)
- Electrolite Tests (0)
- Electrolyte tests (1)
- Erectile Dysfunction (8)
- Erectile Dysfunction Lab Tests (9)
- Español (1)
- Estradiol Estrogen Tests for Men (13)
- Estradiol Test (15)
- FSH Fertility Test (3)
- Fasting blood tests (9)
- Fatigue Blood Tests (22)
- Ferritin lab test (6)
- Fertility Tests (8)
- Free T3 Thyroid Test (10)
- Free T4 Thyroid Test (10)
- Free Testosterone Test (7)
- Gift Certificate Discounted Labs (2)
- Growth Hormone Level (2)
- Gynecomastia tests (4)
- HCG Use in Men (7)
- HDL Cholesterol Test (9)
- Heart Disease Blood Tests (14)
- Heavy Metals Test (2)
- Hepatic Function Panel (3)
- High Hematocrit (13)
- Hormone Blood & Lab Tests (15)
- Human Chorionic Gonadotropin hCG in Men (6)
- IGF-1 Lab Test (2)
- Immigration Tests (2)
- Immunity tests (6)
- Inflammation Tests (16)
- Kidney Function (7)
- LH Lab Test (2)
- Lab Test Descriptions (8)
- Lab Test Education (13)
- Lab Test Normal Ranges (4)
- Lab Tests for Children (1)
- Libido Options for Men (13)
- Lipids cholesterol tests (7)
- Low Free T3 (3)
- Low Magnesium Symptoms (1)
- Magnesium Deficiency (1)
- Magnesium Test (1)
- Meaning of low and high lab test values (11)
- Men's Health Lab Tests (22)
- Natural Testosterone (10)
- Parathyroid PTH test (1)
- Pregnenolone Test (1)
- Progesterone (1)
- Prolactin Lab Test (2)
- Prostate Tests (5)
- Reverse T3 Thyroid Test (7)
- SHBG Lab Test (1)
- Saliva Tests (1)
- Sex Hormone Binding Globulin SHBG Test (2)
- TB Test (4)
- TBG lab test (2)
- TRT App to Track Response (1)
- TRT Blood Tests (44)
- TRT Guidelines (3)
- TRT Monitoring (27)
- TRT Side Effects (41)
- TRT Testing (27)
- TSH Thyroid Test (11)
- Testicular Atrophy (5)
- Testosterone Blood Tests (52)
- Testosterone Book (1)
- Testosterone Doctor (8)
- Testosterone Lab Tests (49)
- Testosterone Replacement Monitoring Tests (26)
- Testosterone Side Effect Management (44)
- Testosterone TRT Forums (5)
- Testosterone Tests (57)
- Testosterone in Women (9)
- Thyroid Lab Tests (12)
- Thyroid Tests (14)
- Urine Tests (1)
- Vitamin Blood Tests (12)
- Women's Hormone Tests (18)
- complete lab test panel (9)
- lab tests for women (18)
- liver tests (8)
- muscle diseases (1)
- viral illness (4)




